What is data annotation?
The human activity of tagging content such as text, images, and videos, so that machine learning models can recognize them and use them to generate predictions, is known as data annotation.
When we label data elements, ML models accurately understand what they are going to process and retain that information to automatically process the available information, based on existing knowledge, to make decisions.
Data annotation refers to the process of attributing, tagging, or labeling data. To summarize, data labeling and data annotation are both concerned with labeling or tagging relevant information/metadata in a dataset so that machines can understand what they are. The dataset can take any form, such as an image, an audio file, video footage, or even text. When we label elements in data, ML models accurately comprehend what they are going to process and retain that information in order to automatically process newer information that is built on existing knowledge in order to make timely decisions.
Why is it important to annotate data?
The importance of data annotation comes from the fact that even the smallest error can be disastrous. In other words, human data annotations will need to manually go through each image and determine whether the annotation quality is high enough to teach algorithms.
Data Labeling vs Annotation: Is There a Difference?
Except for the style and type of content tagging that is used, there is a very thin line between data annotation and data labeling. As a result, depending on the AI model and training process, they are frequently used interchangeably to create ML training data sets.
Types of data annotation
- Semantic annotation: Semantic annotation is the process of labeling concepts such as people, places, or company names within a text to assist machine learning models in categorizing new concepts in future texts. This is a critical component of AI training for improving chatbots and search relevance.
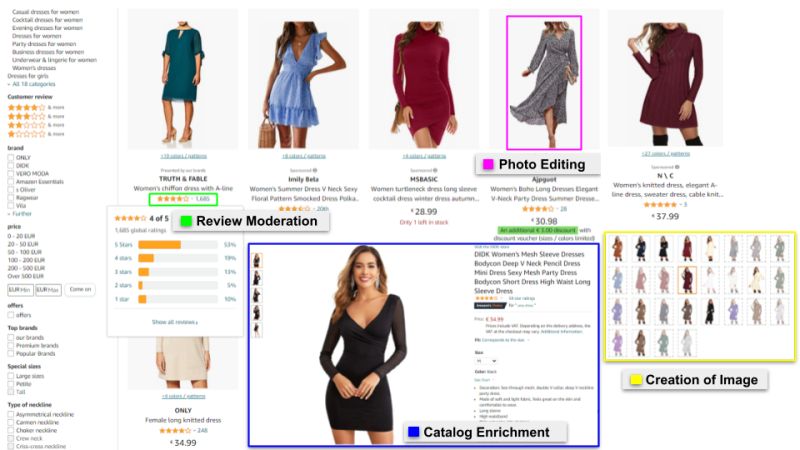
- Image annotation: This type of annotation ensures that machines recognise an annotated area as a distinct object, and it frequently makes use of bounding boxes (imaginary boxes drawn on an image) and semantic segmentation (the assignment of meaning to every pixel). These labeled datasets can be used to help self-driving cars or facial recognition software.

- Video annotation: Video annotation, like image annotation, uses techniques like bounding boxes to recognise movement on a frame-by-frame basis or via a video annotation tool. Data gleaned from video annotation is critical for computer vision models that perform localization and object tracking.
- Text categorization: Text categorization is the process of assigning categories to sentences or paragraphs within a given document based on their topic.
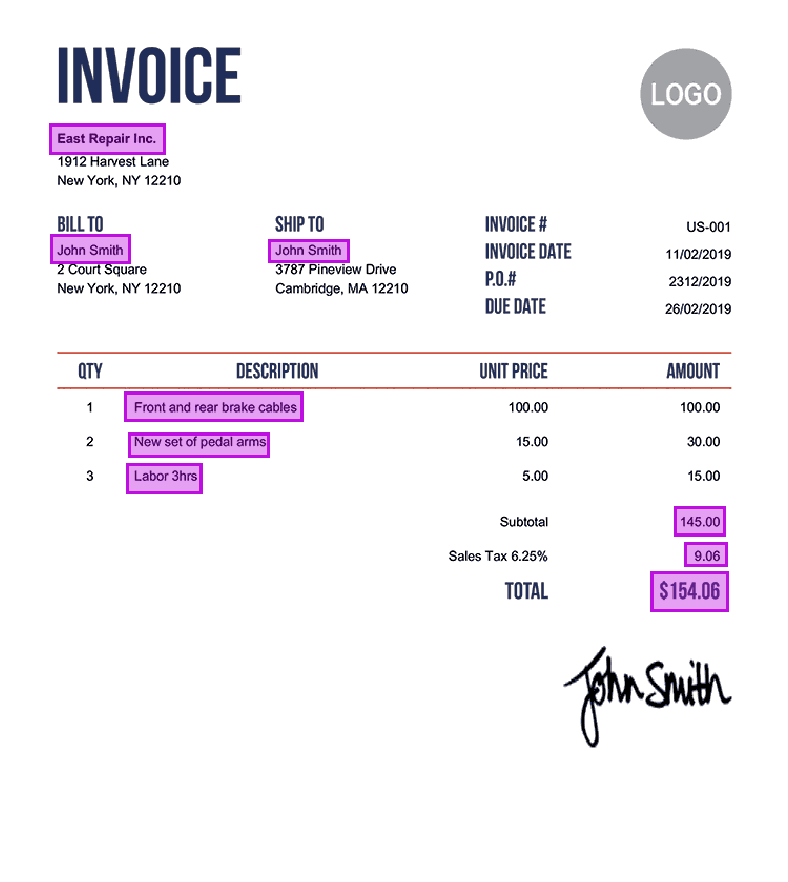
- Entity annotation: The process of assisting a machine in comprehending unstructured sentences. There are numerous techniques that can be used to gain a better understanding, such as Named Entity Recognition (NER), which annotates words within a body of text with predetermined categories (e.g., person, place or thing). Another example is entity linking, in which parts of a text (for example, a company and its headquarters) are tagged as related.

- Timestamps: This is when certain events happen in the video or audio and you need to place a timestamp when this event happened.
- Intent extraction: Intent extraction is the process of labeling phrases or sentences with intent in order to create a library of different ways people use certain words. “How do I make a reservation?” and “Can I confirm my reservation?” contain the same keyword but have different intent. It’s yet another important tool for teaching chatbot algorithms to make decisions based on customer requests.
- Phrase chunking: The process of tagging parts of speech with their grammatical definition is known as phrase chunking (e.g., noun or verb).
- Semantic segmentation: Image segmentation is a more sophisticated type of data labeling. It means dividing our image into various parts, called segments. By dividing the image into segments, we can gain a far deeper understanding of what is happening in the image and how various objects are related.

4 Key Steps in Data Labeling and Data Annotation Process
To categorically train AI models, data labeling is a detailed process that includes the following steps:
- Obtaining Data Sets through various strategies, such as in-house, open source, and vendor.
- The actual labeling and annotation is the second and most important step in the process. Data sets are labeled based on computer vision, deep learning, and natural language processing capabilities.
- The data is sent to the third stage of the process, which is quality assurance, after it has been checked, tagged, labeled, or annotated. As part of deployment, testing and evaluating produced models to determine intelligence.
- Obtaining acceptable model quality and then releasing it for widespread use.
Data Annotation Use Cases
1. Improving the Quality of Search Engine Results for a Wide Range of Users
Users expect comprehensive information from search engines. To do so, their algorithms must process large amounts of labeled datasets in order to provide the correct answer. Take Microsoft’s Bing, for example. Because it serves multiple markets, the vendor must ensure that the search engine’s results are appropriate for the user’s culture, line of business, and other factors.
2. Local Search Evaluation Refinement
While search engines cater to a global audience, vendors must also ensure that users receive highly concentrated results. Data annotators can assist with this by geotagging information, images, and other content.
3. Enhancing Social Media Content Relevance
Social media platforms, like search engines, must provide users with personalized content recommendations. Annotating data can assist developers in classifying and categorizing content for relevance. Consider categorizing which content a user is likely to consume or appreciate based on his or her viewing habits and which he or she would find relevant based on where he or she lives or works.
What is the importance of using data annotation in ML?
- Improved end-user experience
Data annotation, when done correctly, can significantly improve the quality of automated processes and apps, thereby improving the overall experience with your products. If your websites use chatbots, you will be able to provide timely and automatic assistance to your customers 24 hours a day, seven days a week, without requiring them to speak with a customer support employee who may be unavailable outside of working hours.
Furthermore, virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa have greatly increased the utility of smart devices through voice recognition software.
- Improves the accuracy of the output
Because of the large number of man-hours invested in the process, human-annotated data is usually error-free. Search engines can provide more relevant results based on the preferences of users by annotating data. When an annotation is applied to a social media platform’s algorithm, it is possible to customize the feeds of its users.
In general, annotation improves the quality, speed, and security of computer systems.
What are the main challenges of data annotation?
Cost of data annotation: Data annotation can be done manually or automatically. However, manually annotating data takes a lot of time and effort, and you must also maintain the data’s quality.
Annotation accuracy: Human errors can result in poor data quality, which has a direct impact on the prediction of AI/ML models. According to Gartner’s research, poor data quality costs businesses 15% of their revenue.
Final Thoughts
One of the big factors of artificial intelligence and machine learning development is data annotation. As technology advances, almost every industry will need to use annotations to improve the quality of their systems and stay on top of the latest trends.
Since data annotation is very important for the overall success of your AI projects, you should carefully choose your service provider. TagX offers data annotation services for machine learning. Having a diverse pool of accredited professionals, access to the most advanced tools, cutting-edge technologies, and proven operational techniques, we constantly strive to improve the quality of our client’s AI algorithm predictions. Regardless of the type of data you intend to get annotations for, you could find that veteran team in us to meet your demands and goals. Get your AI models optimized for learning with us.