Autonomous vehicles are still working towards reaching the stage of full autonomy. A fully functioning and safe autonomous vehicle must be competent in a wide range of machine learning processes before it can be trusted to drive on its own. From processing visual data in real-time to safely coordinating with other vehicles, the need for AI is essential. Self-driving cars could not do any of this without a huge volume of different types of training data, created and tagged for specific purposes.
Due to the several existing sensors and cameras, advanced automobiles generate a tremendous amount of data. We cannot use these datasets effectively unless they are correctly labeled for subsequent processing. This could range from simple 2D bounding boxes all the way to more complex annotation methods, such as semantic segmentation.
There are various image annotation types such as Polygons, bounding boxes, 3D cuboids, Semantic Segmentation, Lines, and Splines that can be incorporated into autonomous vehicles. These annotation methods help in achieving greater accuracy for autonomous driving algorithms. However, which annotation method is best suited for you must be chosen according to the requirements of your project.
Types of Annotation for Autonomous Driving
Below we have discussed all types of annotation required to make the vehicle autonomous.
2D bounding Box Annotation
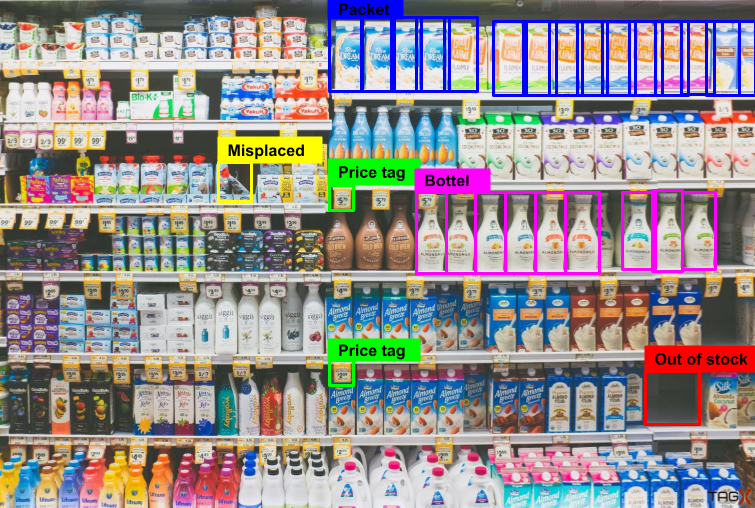
The bounding box annotation technique is used to map objects in a given image/video to build datasets thereby enabling ML models to identify & localize objects.2D boxing is rectangular, and among all the annotation tools, it is the simplest data annotation type with the lowest cost. This annotation type is preferred in less complex cases and also if you are restricted by your budget. This is not trusted to be the most accurate type of annotation but saves a lot of labeling time. Common labeling objects include: Vehicles, Pedestrian, Obstacles, Road signs, Signal lights, Buildings, Parking zone
3D Cuboid Annotation
Similar to the bounding boxes that were previously discussed, this type involves the annotator drawing boxes around the objects in an image. The bounding boxes in this sort of annotation, as the name implies, are 3D, allowing the objects to be annotated on depth, width, and length (X, Y, and Z axes). An anchor point is placed at each edge of the object after the annotator forms a box around it. Based on the characteristics of the object and the angle of the image, the annotator makes an accurate prediction as to where the edge maybe if it is missing or blocked by another object. This estimation/ annotation plays a vital role in judging the distance of the object from the car based on the depth and detecting the object’s volume and position.
Polygon Annotation
It can occasionally be challenging to add bounding boxes around specific items in an image due to their forms and sizes. In photos and movies with erratic objects, polygons provide precise object detection and localization. Due to its precision, it is one of the most popular annotation techniques. However, the accuracy comes at a price because it takes longer than other approaches. Beyond a 2D or 3D bounding box, irregular shapes like people, animals, and bicycles need to be annotated. Since polygonal annotation allows the annotator to specify additional details such as the sides of a road, a sidewalk, and obstructions, among other things, it can be a valuable tool for algorithms employed in autonomous vehicles.
Semantic Segmentation
We’ve looked at defining objects in images up to this point, but semantic segmentation is far more accurate than other methods. It deals with assigning a class to each pixel in an image. For a self-driving automobile to function well in a real-world setting, it must comprehend its surroundings. The method divides the items into groups like bicycles, people, autos, walkways, traffic signals, etc. Typically, the annotator will have a list made up of these. In conclusion, semantic segmentation locates, detects, and classifies the item for computer vision. This form of annotation demands a high degree of accuracy, where the annotation must be pixel-perfect.
Lines and Splines Annotation
In addition to object recognition, models need to be trained on boundaries and lanes. To assist in training the model, annotators drew lines in the image along the lanes and edges. These lines allow the car to identify or recognize lanes, which is essential for autonomous driving to succeed since it enables the car to move through traffic with ease while still maintaining lane discipline and preventing accidents.
Video Annotation
The purpose of video annotation is to identify and track objects over a collection of frames. The majority of them are utilized to train predictive algorithms for automated driving. Videos are divided into thousands of individual images, with annotations placed on the target object in each frame. In complicated situations, single frame annotation is always employed since it can ensure quality. At this time, machine learning-based object tracking algorithms have already helped in video annotation. The initial frame’s objects are annotated by the annotator, and the following frames’ items are tracked by the algorithm. Only when the algorithm doesn’t work properly does the annotator need to change the annotation. As labor costs decrease, clients can save a greater amount of money. In basic circumstances, streamed frame annotation is always employed.
Use Cases of Autonomous Driving
The main goal of data annotation in automotive is to classify and segment objects in an image or video. They help achieve precision, which to automotive is important, given that it is a mission-critical industry, and the accuracy, in turn, determines user experience. This process is essential because of the use cases it enables:
- Object and vehicle detection: This crucial function allows an autonomous vehicle to identify obstacles and other vehicles and navigate around them. Various types of annotation are required to train the object detection model of autonomous driving so that it can detect persons, vehicles, and other obstacles coming in its way.
- Environmental perception: Annotators use semantic segmentation techniques to create training data that labels every pixel in a video frame. This vital context allows the vehicle to understand its surroundings in more detail. It’s important to have a complete understanding of its location and everything surrounding it to make a safe drive.
- Lane detection: Autonomous vehicles need to be able to recognize road lanes so that they can stay inside of them. This is very important to avoid any accidents. Annotators support this capability by locating road markings in video frames.
- Understanding signage: The vehicle must be able to recognize all the signs and signals on the road to predict when and where to stop, take a turn, and many related objectives. Autonomous vehicles should automatically detect road signs and respond to them accordingly. Annotation services can enable this use case with careful video labeling.
Conclusion
Although it takes a lot of effort, delivering Ground Truth quality annotation for self-driving cars is crucial to the project’s overall success. Get the best solutions by using precise annotations created by TagX to train and validate your algorithms.
We are the data annotation experts for autonomous driving. We can help with any use case for your automated driving function, whether you’re validating or training your autonomous driving stack. Get in contact with our specialists to learn more about our automobile and data annotation services as well as our AI/ML knowledge.